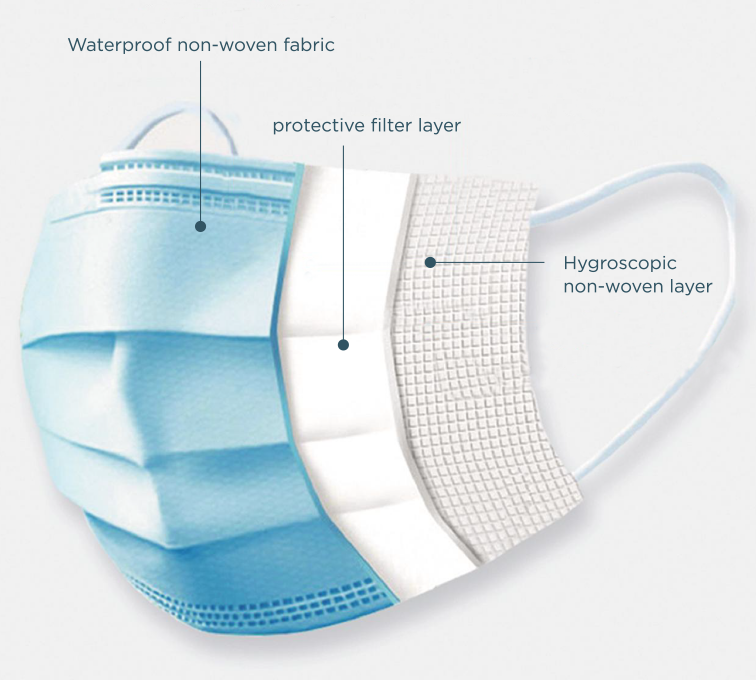
Masks
Provision of a smart simple explanation to ensure you get the mask that meets your need.
P2 relates to particle size of 2.5 microns and is the European standard – it is not equivalent to LEVEL 2. P2 has filtration but no fluid resistance. Why is this important?
• Clinicians, dental and medical, work in an aerosolised environment.
• Microorganisms remain in the air for up to 30 minutes after the patients surgery is completed and CoV-19 remains for 3 hours.
• Ensure you are protected against airborne virus
• 3M 8110 and 8210 masks are labelled as P2 N95 but these are not fluid resistant and not for medical use. They are industrial masks suitable e.g. for bushfires, builders etc.
Level 1 are a low-level barrier protection for general use for low-risk, non-surgical procedures and examinations that do not involve aerosols, sprays and fluids for single use with 80 mmHg resistance to penetration by synthetic blood. The filtration effectiveness is 95% for particles 3.0 microns BFE (Bacterial Filtration Efficiency standard) and 0% for particles 0.1 microns PFE (Particle Filtration Efficiency).
Level 2 masks have a middle layer and are fluid resistant – 120 mmHg. Suitable for oral examinations for medium risk patients and procedures involving blood splatter, moderate levels of spray, and lab work with exposure to blood or contaminated materials. The filtration effectiveness is greater than 98% for particles 3.0 microns BFE and greater than 98% for 0.1 microns PFE.
Level 3 are high barrier surgical masks ideal for treating high-risk patients and all surgical procedures involving high levels of spray, splatter, moisture and airborne particles e.g. with use of ultrasonic scalers, high speed drills, air polishers and oral surgeries. The minimum pressure (fluid resistance) is 160 mmHg and filtration effectiveness is greater than 98% for particles 3.0 microns BFE and greater than 98% for 0.1 microns PFE.
Gowns
Surgical Gowns
A few of the many terms that have been used to refer to gowns intended for use in health care settings, include surgical gowns, isolation gowns, surgical isolation gowns, non-surgical gowns, procedural gowns, and operating room gowns.
In 2004, the FDA recognized the consensus standard American National Standards Institute/Association of the Advancement of Medical Instrumentation (ANSI/AAMI) PB70:2003, “Liquid barrier performance and classification of protective apparel and drapes intended for use in health care facilities.”
New terminology in the standard describes the barrier protection levels of gowns and other protective apparel intended for use in health care facilities and specifies test methods and performance results necessary to verify and validate that the gown provides the newly defined levels of protection:
• Level 1: Minimal risk, to be used, for example, during basic care, standard isolation, cover gown for visitors, or in a standard medical unit
• Level 2: Low risk, to be used, for example, during blood draw, suturing, in the Intensive Care Unit (ICU), or a pathology lab
• Level 3: Moderate risk, to be used, for example, during arterial blood draw, inserting an Intravenous (IV) line, in the Emergency Room, or for trauma cases
• Level 4: High risk, to be used, for example, during long, fluid intense procedures, surgery, when pathogen resistance is needed or infectious diseases are suspected (non-airborne) such as ICU.
Non-Surgical Gowns
Non-surgical gowns are Class I devices intended to protect the wearer from the transfer of microorganisms and body fluids in low or minimal risk patient isolation situations. Non-surgical gowns are not worn during surgical procedures, invasive procedures, or when there is a medium to high risk of contamination.
Surgical Gowns
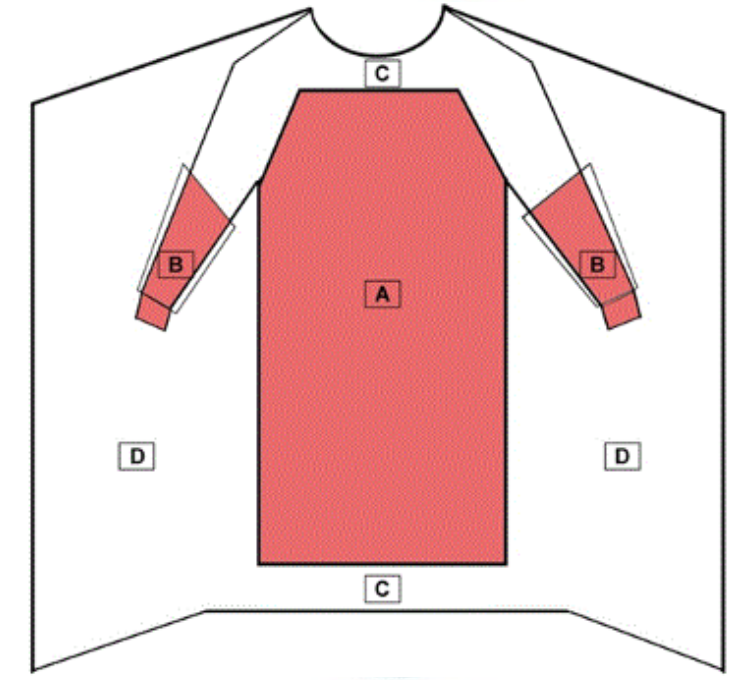
A surgical gown is a personal protective garment intended to be worn by health care personnel during surgical procedures to protect both the patient and health care personnel from the transfer of microorganisms, body fluids, and particulate matter. Because of the controlled nature of surgical procedures, critical zones of protection have been described by national standards. The critical zones include the front of the body from top of shoulders to knees and the arms from the wrist cuff to above the elbow. Surgical gowns can be used for any risk level (Levels 1-4). All surgical gowns must be labelled as a surgical gown.
Surgical Isolation Gowns
Surgical isolation gowns are used when there is a medium to high risk of contamination and a need for larger critical zones than traditional surgical gowns.
All seams must have the same liquid barrier protection as the rest of the gown. Additionally, the fabric of the surgical isolation gown should cover as much of the body as is appropriate for the intended use.